📝 Guest Post: The Evolution of Extreme LLM Compression: From QuIP to AQLM with PV-Tuning*
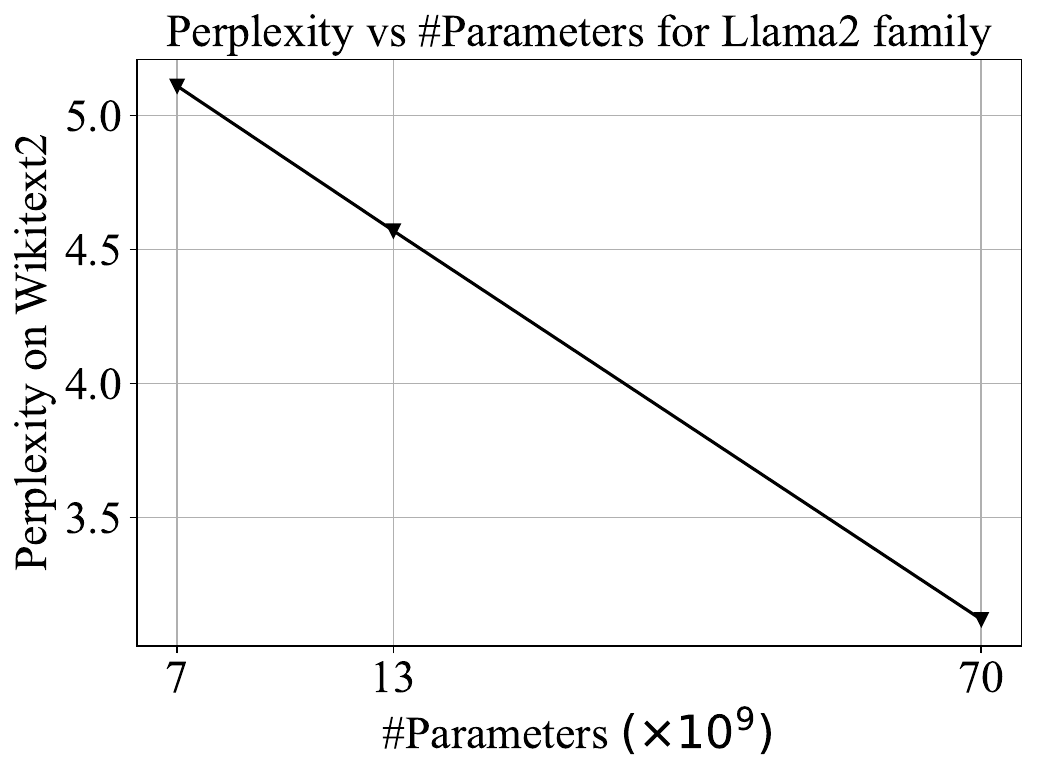
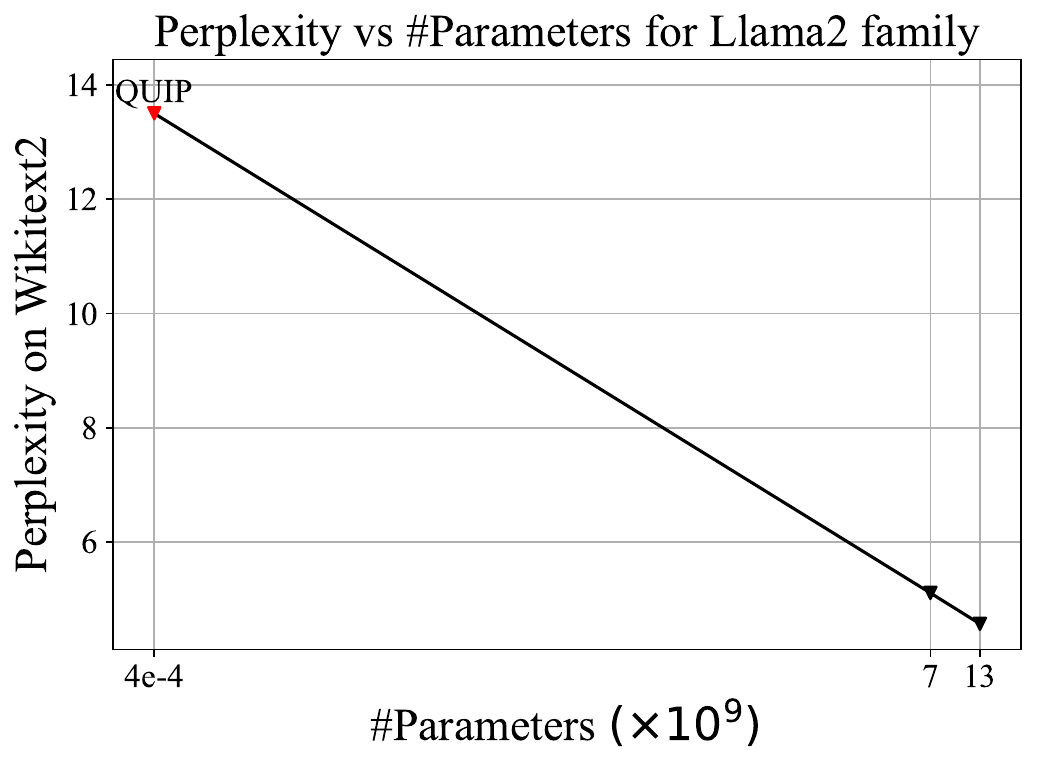
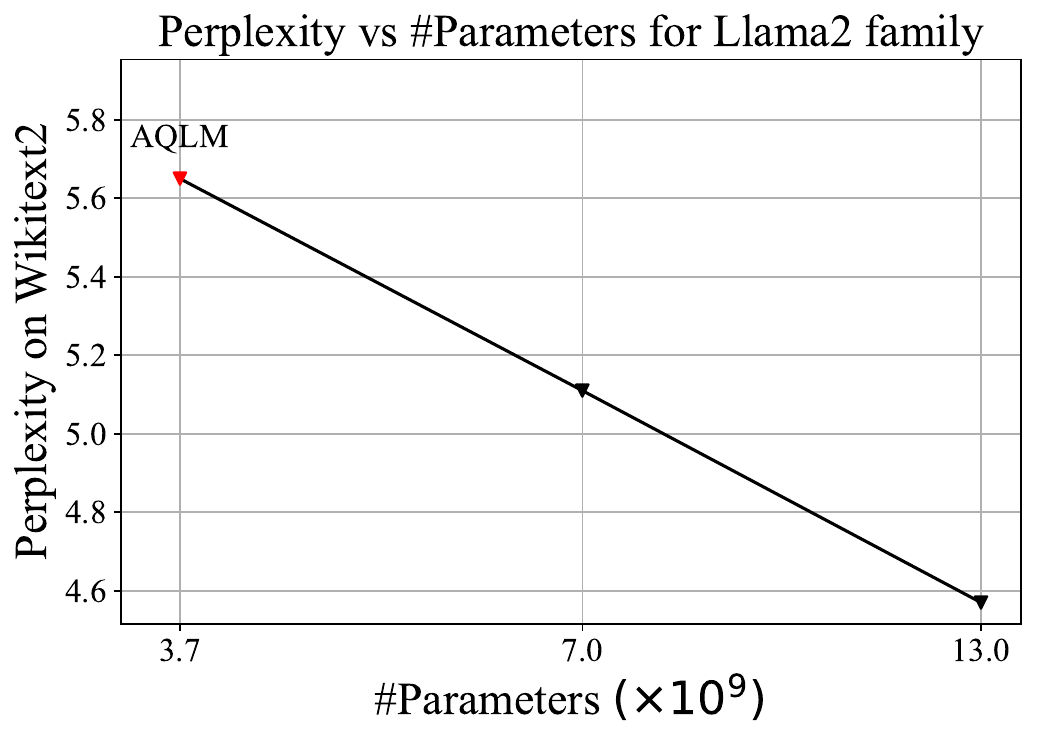
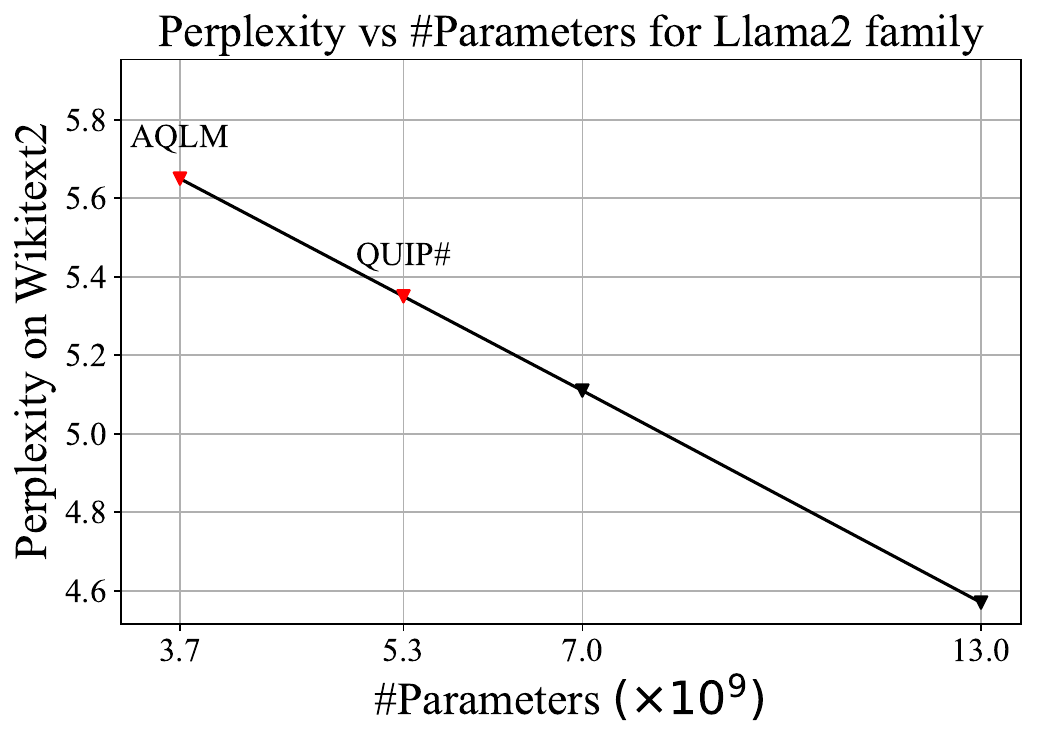
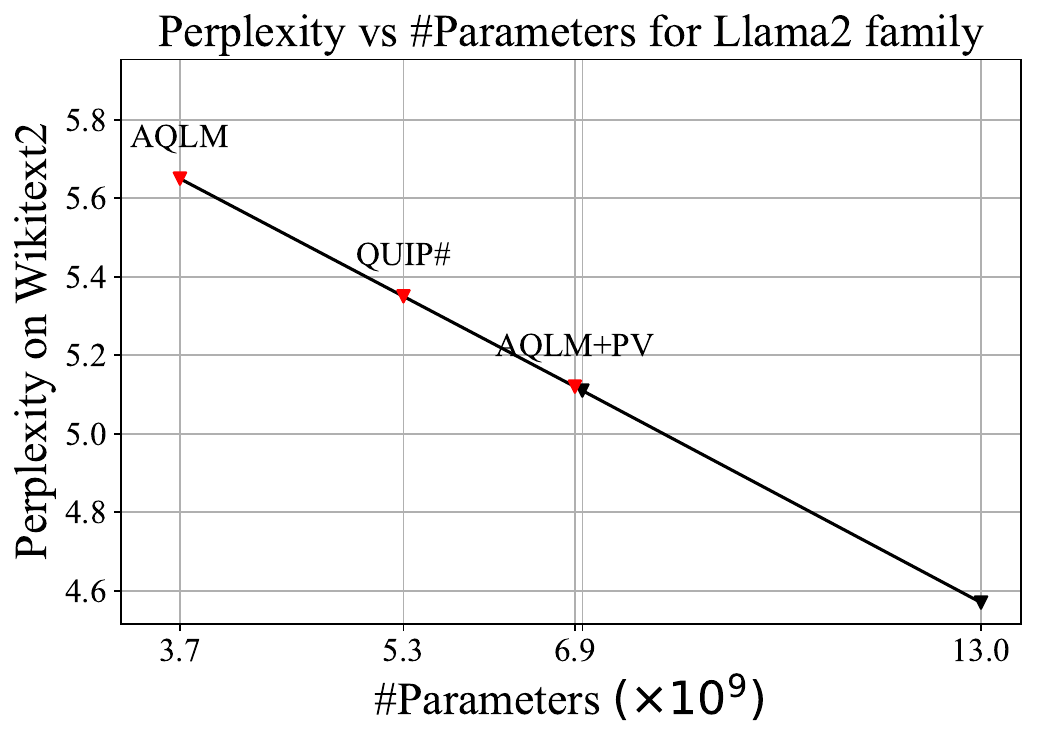
Was this email forwarded to you? Sign up here In this guest post, Vladimir Malinovskii discusses the intense competition between research teams at Yandex, IST Austria, KAUST, and Cornell University in developing cutting-edge neural network compression techniques. Highlighting methods like AQLM, QuIP, and their evolutions, the post explores the progress in compressing LLMs to 2-bit formats, enabling significant reductions in model size while maintaining quality, ultimately making large models accessible on standard hardware. We live in the era of Large Language Models (LLMs), with companies increasingly deploying models with billions of parameters. These expansive models unlock new possibilities for users but come with high deployment costs and complexity, especially on personal computers. As a result, researchers and engineers often train these large models first and then compress them, while trying to minimize quality loss. Models are released in the float16 format, where 16 bits are allocated for each weight. Two years ago, technological advancement got us to the point where we can reliably compress neural networks down to 4 bits using techniques like GPTQ. However, the progress doesn't stop here, as the research community is now actively seeking methods to reduce model size eightfold, down to 2 bits. A little while ago, the Yandex Research team joined efforts with their colleagues from IST Austria and KAUST to introduce a new method of achieving 8x compression through the combined use of AQLM and PV-Tuning. This method has been made publicly available to software developers and researchers, with the code published in a GitHub repository. Examples of popular open-source models that were compressed using this method can be downloaded here. For fine-tuning a compressed neural network, take a look at these training materials. In the meantime, we'd like to shed some light on how the method was developed thanks to a brief (albeit very exciting!) "rivalry" between two research teams and their state-of-the-art compression algorithms: QuIP and AQLM. Competition fuels innovation, and this rapidly evolving story is a prime example. Every other month brings new breakthroughs, optimizations, and ingenious solutions. Sit back and enjoy! MethodologyIn our example, we'll be using Llama2 13b. Along with it, Meta released two more models sized 7b and 70b. In academic research, perplexity is typically used to assess the quality of compressed models. This metric measures how perplexed (hence the name) a neural network gets after seeing a correctly written text. Lower perplexity means a better model. For this article, we've chosen a different primary metric: effective model size. All three Llama2 models fall on the same line when plotting perplexity against model size, so we can report a more intuitive metric. Quantization of LLMs With GuaranteesIn mid-2023, a group of scientists from Cornell University published an article titled QuIP, where the authors seriously discuss for the first time the possibility of compressing neural networks by a factor of 8. The idea is that 99% of weights in large language models behave similarly and can be easily compressed with minimal loss. However, the remaining 1% — outliers — significantly deviate from the norm and lead to inaccuracies during compression. The QuIP authors devised a technique to shuffle these weights, effectively solving the outlier problem. The algorithm compresses Llama2 13b to a perplexity of 13.5. At first glance, this may seem like a poor result, as it corresponds to a model with a mere size of 0.43M parameters. But this was the first time the perplexity remained in the double digits after compression. For reference, GPTQ compresses the same model to a perplexity of 123. So, what QuIP managed to achieve was nothing short of a breakthrough. Extreme Compression of LLMs via Additive QuantizationSix months later, in January 2024, researchers from Yandex and the Institute of Science and Technology Austria (ISTA) published a paper on additive quantization for language models (AQLM). The method relies on additive quantization proposed in 2014 by Artem Babenko, Head of Yandex Research — back then, it was intended to help the company's search engine needs. Ten years later, this technology was repurposed to compress large language models while maintaining maximum quality. AQLM compresses Llama 13b to a perplexity corresponding to the 3.7b model. This was a significant improvement over QuIP — a model like that was now actually usable. A Close Competition — Upgrade From QuiP to QuIP#Just a month later, researchers from Cornell struck back with a new study titled "QuIP#." The authors refined their method with fine-tuning and other optimizations, showing that you can fine-tune a compressed neural network on a calibrated dataset to significantly reduce compression error without changing the model's representation format. QuIP# performed better than AQLM, improving the SOTA quantization of the Llama2-13b model to an effective size of 5.3B parameters. A New Chapter for AQLMIn late May, a joint study from the creators of AQLM and researchers from King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) sees light. The authors propose an advanced fine-tuning algorithm — PV-Tuning — to improve on the old AQLM. While the QuIP# paper suggests fine-tuning only continuous parameters with gradients, PV-Tuning modifies all model parameters, including discrete ones. In terms of quality, this is the best algorithm for 2-bit quantization to date. It compresses the Llama 13b model to an effective size of 6.9B, falling just a bit short of the 7b model. Every year, neural network quantization becomes more and more efficient: inference costs are going down exponentially, and large models with open weights can now be launched on regular hardware. A few years ago, one could only dream of launching a large model like Llama3 70b on an RTX 3090. In 2024, that's already a reality. Healthy competition among researchers is a catalyst for technological advancement, driving innovation and the development of creative approaches. How will the story unfold from here? Time will tell! And we have a feeling it won't be long. *This post was written by Vladimir Malinovskii, ML resident @ Yandex Research, and originally published here. We thank Yandex for their insights and ongoing support of TheSequence.You’re on the free list for TheSequence Scope and TheSequence Chat. For the full experience, become a paying subscriber to TheSequence Edge. Trusted by thousands of subscribers from the leading AI labs and universities. |
Older messages
Edge 421: A New Series About State Space Models
Tuesday, August 13, 2024
Diving into the best alternative to transformer models. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
You Need to Know About Groq
Sunday, August 11, 2024
A $640 million funding round to accelerate its fast inference chips. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
📝 Guest Post: RAG Evaluation Using Ragas*
Friday, August 9, 2024
In this guest post, the teams from Zilliz and Ragas discuss key RAG evaluation metrics, their calculation, and implementation using the Milvus vector database and the Ragas package. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
Edge 420: Inside FlashAttention-3, The Algorithm Pushing the New Wave of Transformers
Thursday, August 8, 2024
The new algorithm takes full advantage of the capabilities of H100 GPUs. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
Edge 419: Everything You Need to Know About Autonomous Agents in 19 Posts
Tuesday, August 6, 2024
A summary of our long series about automous agents. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
You Might Also Like
Import AI 399: 1,000 samples to make a reasoning model; DeepSeek proliferation; Apple's self-driving car simulator
Friday, February 14, 2025
What came before the golem? ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
Defining Your Paranoia Level: Navigating Change Without the Overkill
Friday, February 14, 2025
We've all been there: trying to learn something new, only to find our old habits holding us back. We discussed today how our gut feelings about solving problems can sometimes be our own worst enemy
5 ways AI can help with taxes 🪄
Friday, February 14, 2025
Remotely control an iPhone; 💸 50+ early Presidents' Day deals -- ZDNET ZDNET Tech Today - US February 10, 2025 5 ways AI can help you with your taxes (and what not to use it for) 5 ways AI can help
Recurring Automations + Secret Updates
Friday, February 14, 2025
Smarter automations, better templates, and hidden updates to explore 👀 ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
The First Provable AI-Proof Game: Introducing Butterfly Wings 4
Friday, February 14, 2025
Top Tech Content sent at Noon! Boost Your Article on HackerNoon for $159.99! Read this email in your browser How are you, @newsletterest1? undefined The Market Today #01 Instagram (Meta) 714.52 -0.32%
GCP Newsletter #437
Friday, February 14, 2025
Welcome to issue #437 February 10th, 2025 News BigQuery Cloud Marketplace Official Blog Partners BigQuery datasets now available on Google Cloud Marketplace - Google Cloud Marketplace now offers
Charted | The 1%'s Share of U.S. Wealth Over Time (1989-2024) 💰
Friday, February 14, 2025
Discover how the share of US wealth held by the top 1% has evolved from 1989 to 2024 in this infographic. View Online | Subscribe | Download Our App Download our app to see thousands of new charts from
The Great Social Media Diaspora & Tapestry is here
Friday, February 14, 2025
Apple introduces new app called 'Apple Invites', The Iconfactory launches Tapestry, beyond the traditional portfolio, and more in this week's issue of Creativerly. Creativerly The Great
Daily Coding Problem: Problem #1689 [Medium]
Friday, February 14, 2025
Daily Coding Problem Good morning! Here's your coding interview problem for today. This problem was asked by Google. Given a linked list, sort it in O(n log n) time and constant space. For example,
📧 Stop Conflating CQRS and MediatR
Friday, February 14, 2025
Stop Conflating CQRS and MediatR Read on: my website / Read time: 4 minutes The .NET Weekly is brought to you by: Step right up to the Generative AI Use Cases Repository! See how MongoDB powers your