📝 Guest Post: Enhancing ChatGPT's Efficiency – The Power of LangChain and Milvus*
Was this email forwarded to you? Sign up here In this guest post, the Zilliz team lists the challenges of using ChatGPT and explores how to enhance the intelligence and efficiency of ChatGPT to overcome the obstacles of hallucinations. While ChatGPT has gained significant popularity, with many individuals utilizing its API to develop their chatbots or explore LangChain, it's not without its challenges.
Enhancing ChatGPT's intelligence is where the combination of LangChain and Milvus comes into play. With the integration of LangChain and Milvus, LLMs can harness vector stores’ power to increase intelligence and efficiency. How does all of this work? Let's dive into the power of LangChain and Milvus in LLM applications, then explore how to build and enhance your own AI Generated Content (AIGC) application. LangChain for LLM-powered ApplicationLangChain is a framework for developing applications powered by language models. The LangChain framework is designed around the following principles:
LangChain's robust framework consists of a range of modules, such as Models, Prompts, Memory, Indexes, Chains, Agents, and Callbacks, which are the core abstractions that can view as the building blocks of any LLM-powered application. For each module, LangChain provides standard, extendable interfaces. LangChain also provides external integrations and even end-to-end implementations for off-the-shelf use. The LLM wrapper is at the heart of LangChain functionality, offering a host of LLM providers such as OpenAI, Cohere, Hugging Face, etc. It provides a standard interface to all LLMs and includes common tools for working with them. Vector Database for LLMsLangChain offers an impressive range of Large Language Models (LLMs) to cater to diverse needs. But that's not all. LangChain goes beyond the basics by integrating various vector databases such as Milvus, Faiss, and others to enable semantic search functionality. Through its VectorStore Wrapper, LangChain standardizes the necessary interfaces to simplify the loading and retrieval of data. For instance, using the Milvus class, LangChain allows the storage of feature vectors representing documents using the Delving deeper into the subject, we realize that vector databases have a significant role in LLM applications, as evident from the chatgpt-retrieval-plugin. But that's not where their utility ends. Vector databases have a plethora of other use cases, making them an indispensable component of LLM applications:
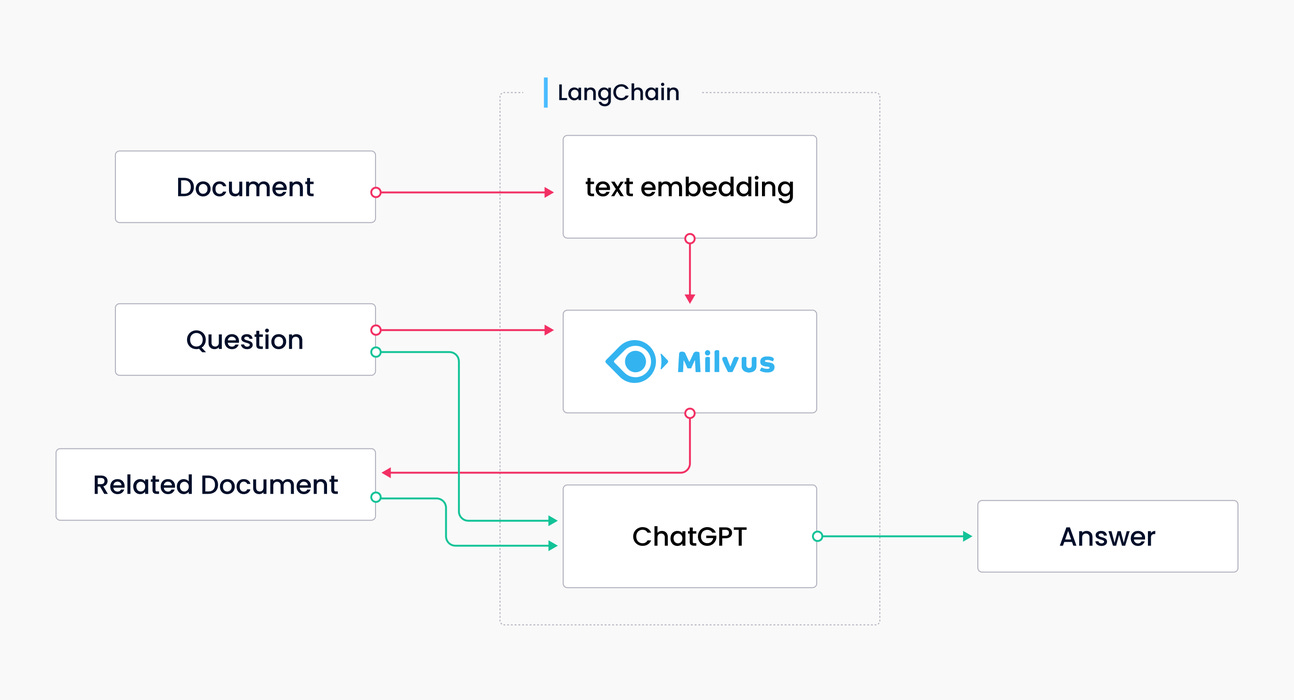
If you want to learn more about how the Milvus vector database powers Auto-GPT, you can learn by reading this article. In the following section, you will learn how LangChain and Milvus can address hallucinations. Why LangChain + Milvus Can Resolve HallucinationsIn artificial intelligence, there is a saying that the system will frequently generate "hallucinations," which means fabricating facts unrelated to reality. Some even describe ChatGPT as "a confident guy who can write very convincing nonsense," and the hallucination problem undermines the credibility of ChatGPT. Vector Databases illustrated in the following diagram address the issue of hallucinations. First, store the official documents as text vectors in Milvus, and search for relevant documents in response to the question (the orange line in the diagram). ChatGPT answers the question based on the correct context, resulting in the expected answer (the green line in the diagram). The example above shows that combining Milvus and ChatGPT is very simple. There's no need to label data, train or develop it, or fine-tune it – you need to convert text data into vector data and insert it into Milvus. The LangChain-Milvus-ChatGPT combo creates text storage, and the final answer is derived from referencing the content in the document library. This ensures the chatbot is fed with the correct knowledge, effectively reducing the likelihood of errors. For example, as a community administrator, when I need to answer community-related questions, I can store all the documents from Milvus's official documentation. When a user asks, "How to use Milvus to build a chatbot," the chatbot will answer the question based on the official documentation, telling the user that it provides examples of building applications and extracting relevant documents. This type of response is reliable. In short, we don't need to retrain or process everything; we need to feed the necessary contextual knowledge to ChatGPT. When we send a request, the robot can provide context related to the official content. Are you feeling excited after discovering the power of Milvus and LangChain for ChatGPT? If yes, then get ready to take your application development. Let's team up and create an enhanced chatbot by using the incredible capabilities of LangChain and Milvus combined! Build Your Own Application with LangChain and Milvus0. PrerequisitesFirst, install LangChain using the command 1. Load Data for Knowledge BaseFirst, we need to load data into a standard format. In addition to loading the text, we need to chunk it up into small pieces. This is necessary to ensure we only pass the most minor, most relevant pieces of text to the language model. Next, now that we have small chunks of text, we need to create embeddings for each piece of text and store them in a vector store. Creating embeddings is done so that we can use the embeddings to find only the most relevant pieces of text to send to the language model. This is done with the following lines. Here we use OpenAI’s embeddings and Zilliz Cloud. 2. Query DataSo now that we have loaded the data, we can use it in a question-answering chain. This involves searching for documents related to our given query from the knowledge base. To accomplish this, use the Then run The code below uses OpenAI as the LLM. When running, the QAChain receives Why Milvus is Better for the AIGC ApplicationSo if you want to make your Artificial Intelligence-Generated Content (AIGC) applications more reliable, having a vector database representing text is necessary. But why choose the Milvus vector database?
Next Step for Your ApplicationIn the realm of AI, constantly new advances and game-changing technologies can elevate your application to the next level. Here, we'll go over two ways to improve your application: implementing GPTCache and tuning embedding models and prompts. This can improve performance and search quality, set your application apart, and provide a better user experience. 1. Improve your AIGC Application performance – GPTCacheIf you want to optimize the performance and save costs for your AIGC application, check out GPTCache. This innovative project is designed to create a semantic cache for storing LLM responses. So, how does this help? By caching responses to LLMs, and vector database can retrieve similar questions to get the cached response, your application can quickly and accurately answer users. With GPTCache, accessing cached answers becomes a breeze — no more redundant response generations, ultimately saving time and computational resources. GPTCache goes a step further by improving the overall user experience. Providing quicker and more accurate answers will satisfy your answer, and your application will be more successful. 2. Improve your search quality – Tune your Embedding Models and PromptsIn addition to utilizing GPTCache, fine-tuning your embedding models and prompts can improve the quality of your search results. Embedding models are a crucial component of AI applications, as they are the building blocks that translate text into numerical vectors, which deep learning can process. By tuning your embedding models, you can improve the accuracy and relevance of your semantic search results. This involves adjusting the models to prioritize specific keywords and phrases and tweaking their weighting and scoring mechanisms better to reflect the needs and preferences of your target audience. With a well-trained embedding model, your AIGC application can accurately interpret and categorize user input, leading to more accurate search results. Apart from that, the prompts used in the applications play an essential role in improving the quality of search results. Prompts are the phrases that your AI uses to prompt users for input, such as "How can I help you today?" or "What's on your mind?". By testing and modifying these prompts, you can improve the quality and relevance of your search results. For example, if your application is geared towards a specific industry or demographic, you may tailor your prompts to reflect the language and terminology used by that group. This helps guide the users towards more relevant search queries, leading to a more satisfactory experience by matching their needs more accurately. By refining prompts to fulfill user requirements, you can help them achieve more successful searches, thus leading to a more satisfied user base. In the endIn summary, LangChain and Milvus are the perfect recipes for developers creating LLM-powered applications from scratch. LangChain offers a standard and user-friendly interface for LLMs, while Milvus delivers remarkable storage and retrieval capabilities. LangChain and Milvus can enhance the intelligence and efficiency of ChatGPT, which helps you go beyond the obstacles of hallucinations. Even better, with GPTCache, prompt, and model tuning technologies, we can improve our AI applications in ways never thought possible. As we continue to push the boundaries of AI, let us collaborate and create a brighter future for AIGC to explore the limitless potential of artificial intelligence. *This post was written by the Zilliz team exclusively for TheSequence. We thank Zilliz for their ongoing support of TheSequence.You’re on the free list for TheSequence Scope and TheSequence Chat. For the full experience, become a paying subscriber to TheSequence Edge. Trusted by thousands of subscribers from the leading AI labs and universities. |
Older messages
Edge 297: Tool-Augmented Language Models
Monday, June 12, 2023
Can LLMs master knowledge tools?
The Sequence Chat: Raza Habib, Humanloop on Building LLM-Driven Applications
Monday, June 12, 2023
Humanloop is one of the emerging platforms that allow developers to build large scale applications on top of LLMs.
Meet MiniGPT-4: The Open Source Vision-Language Model that Matches the Performance of GPT-4
Monday, June 12, 2023
The model expands Vicuna with vision capabilities similar to BLIP-2 in one of the most interesting open source releases in the multi-modality space.
Meet the LLM Garden 🪴🌱
Monday, June 12, 2023
With new LLMs being introduced daily, it's hard to stay on top of what's new and easily compare LLMs. So Superwise, Blattner Tech, and TensorOps pooled forces to put together a resource for the
The AlphaDev Milestone: A New Model that is Able to Discover and Improve Algorithms
Monday, June 12, 2023
Sundays, The Sequence Scope brings a summary of the most important research papers, technology releases and VC funding deals in the artificial intelligence space.
You Might Also Like
Import AI 399: 1,000 samples to make a reasoning model; DeepSeek proliferation; Apple's self-driving car simulator
Friday, February 14, 2025
What came before the golem? ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
Defining Your Paranoia Level: Navigating Change Without the Overkill
Friday, February 14, 2025
We've all been there: trying to learn something new, only to find our old habits holding us back. We discussed today how our gut feelings about solving problems can sometimes be our own worst enemy
5 ways AI can help with taxes 🪄
Friday, February 14, 2025
Remotely control an iPhone; 💸 50+ early Presidents' Day deals -- ZDNET ZDNET Tech Today - US February 10, 2025 5 ways AI can help you with your taxes (and what not to use it for) 5 ways AI can help
Recurring Automations + Secret Updates
Friday, February 14, 2025
Smarter automations, better templates, and hidden updates to explore 👀 ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
The First Provable AI-Proof Game: Introducing Butterfly Wings 4
Friday, February 14, 2025
Top Tech Content sent at Noon! Boost Your Article on HackerNoon for $159.99! Read this email in your browser How are you, @newsletterest1? undefined The Market Today #01 Instagram (Meta) 714.52 -0.32%
GCP Newsletter #437
Friday, February 14, 2025
Welcome to issue #437 February 10th, 2025 News BigQuery Cloud Marketplace Official Blog Partners BigQuery datasets now available on Google Cloud Marketplace - Google Cloud Marketplace now offers
Charted | The 1%'s Share of U.S. Wealth Over Time (1989-2024) 💰
Friday, February 14, 2025
Discover how the share of US wealth held by the top 1% has evolved from 1989 to 2024 in this infographic. View Online | Subscribe | Download Our App Download our app to see thousands of new charts from
The Great Social Media Diaspora & Tapestry is here
Friday, February 14, 2025
Apple introduces new app called 'Apple Invites', The Iconfactory launches Tapestry, beyond the traditional portfolio, and more in this week's issue of Creativerly. Creativerly The Great
Daily Coding Problem: Problem #1689 [Medium]
Friday, February 14, 2025
Daily Coding Problem Good morning! Here's your coding interview problem for today. This problem was asked by Google. Given a linked list, sort it in O(n log n) time and constant space. For example,
📧 Stop Conflating CQRS and MediatR
Friday, February 14, 2025
Stop Conflating CQRS and MediatR Read on: my website / Read time: 4 minutes The .NET Weekly is brought to you by: Step right up to the Generative AI Use Cases Repository! See how MongoDB powers your