📝 Guest Post: Zilliz Unveiled Milvus 2.4 at GTC 24, Transforming Vector Databases with GPU Acceleration*
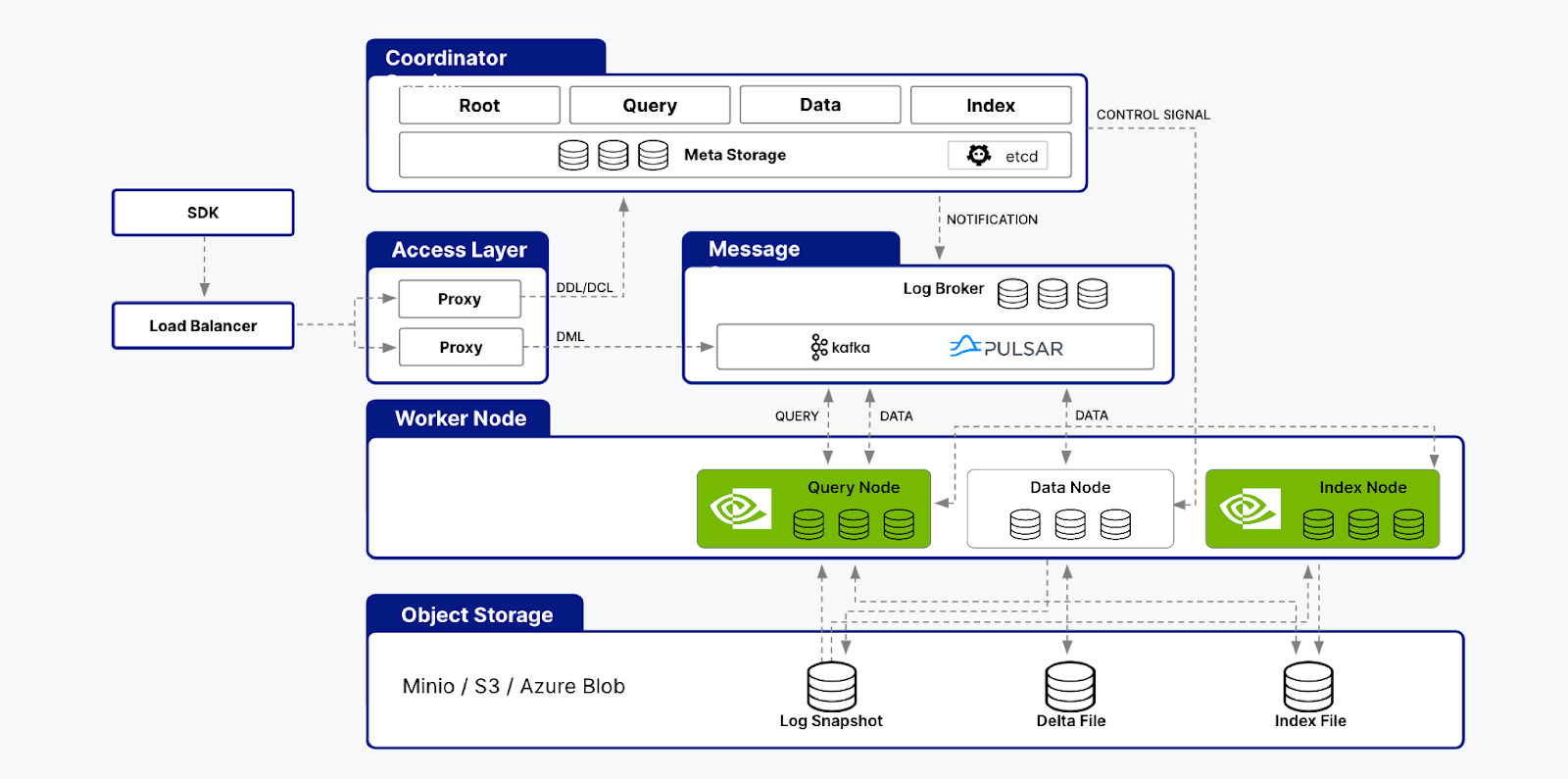
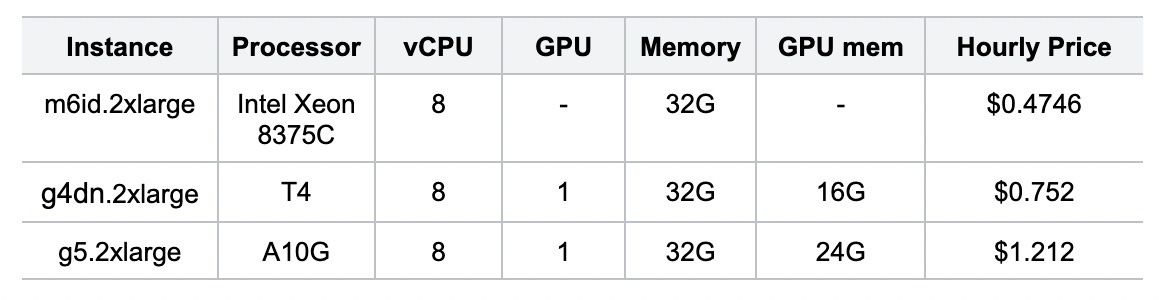
Was this email forwarded to you? Sign up here 📝 Guest Post: Zilliz Unveiled Milvus 2.4 at GTC 24, Transforming Vector Databases with GPU Acceleration*Collaboration with NVIDIA boosts Milvus performance 50xLast week, Zilliz and NVIDIA collaborated to unveil Milvus 2.4 - the world's first vector database accelerated by powerful GPU indexing and search capabilities. This breakthrough release harnesses NVIDIA GPUs’ massively parallel computing power and the new CUDA-Accelerated Graph Index for Vector Retrieval (CAGRA) from the RAPIDS cuVS library. The performance gains enabled by GPU acceleration in Milvus 2.4 are extraordinary. Benchmarks demonstrate up to 50x faster vector search performance than industry standard CPU-based indexes like HNSW. While the open-source Milvus 2.4 is available now, enterprises looking for a fully managed vector database service can look forward to GPU acceleration coming to Zilliz Cloud later this year. Zilliz Cloud provides a seamless experience for deploying and scaling Milvus on major cloud providers like AWS, GCP, and Azure without operational overhead. We asked Charles Xie, the founder and CEO of Zilliz, to tell us more about it. What is MilvusMilvus is an open-source vector database system built for large-scale vector similarity search and AI workloads. Initially created by Zilliz, an innovator in the realm of unstructured data management and vector database technology, Milvus made its debut in 2019. To encourage widespread community engagement and adoption, it has been hosted by the Linux Foundation since 2020. Since its inception, Milvus has gained considerable traction within the open-source ecosystem. With over 26,000 stars and over 260 contributors on GitHub and a staggering 20 million+ downloads and installations worldwide, it has become one of the most widely adopted vector databases globally. Milvus is trusted by over 5,000 enterprises across diverse industries, including AIGC, e-commerce, media, finance, telecom, and healthcare, to power their mission-critical vector search and AI applications at scale. Why GPU AccelerationIn today's data-driven world, quickly and accurately searching through vast amounts of unstructured data is crucial for powering cutting-edge AI applications. From generative AI and similarity search to recommendation engines and virtual drug discovery, vector databases have emerged as the backbone technology enabling these advanced capabilities. However, the insatiable demand for real-time indexing and high throughput has continued to push the boundaries of what's possible with traditional CPU-based solutions. Real-time indexing High throughput At the heart of vector databases lies a core set of vector operations, such as similarity calculations and matrix operations, which are highly parallelizable and computationally intensive. With their massively parallel architecture comprising thousands of cores capable of executing numerous threads simultaneously, GPUs are an ideal computational engine for accelerating these operations. The ArchitectureTo address these challenges, NVIDIA developed CAGRA, a GPU-accelerated framework that leverages the high-performance capabilities of GPUs to deliver exceptional throughput for vector database workloads. Next, let's explore how to integrate the CAGRA algorithm into the Milvus system. Milvus is designed for cloud-native environments and follows a modular design philosophy. It separates the system into various components and layers involved in handling client requests, processing data, and managing the storage and retrieval of vector data. Thanks to this modular design, Milvus can update or upgrade the implementation of specific modules without changing their interfaces. This modularity makes it relatively easy to incorporate GPU acceleration support into Milvus. The modular architecture of Milvus comprises components such as the Coordinator, Access Layer, Message Queue, Worker Node, and Storage layers. The Worker Node itself is further subdivided into Data Nodes, Query Nodes, and Index Nodes. The Index Nodes are responsible for building indexes, while the Query Nodes handle query execution. To leverage the benefits of GPU acceleration, CAGRA is integrated into Milvus’ Index and Query Nodes. This integration enables offloading computationally intensive tasks, such as index building and query processing, to GPUs, taking advantage of their parallel processing capabilities. Within the Index Nodes, CAGRA support has been incorporated into the index building algorithms, allowing for efficient construction and management of high-dimensional vector indexes on GPU hardware. This acceleration significantly reduces the time and resources required for indexing large-scale vector datasets. Similarly, in the Query Nodes, CAGRA is utilized to accelerate the execution of complex vector similarity searches. By leveraging GPU processing power, Milvus can perform high-dimensional distance calculations and similarity searches at unprecedented speeds, resulting in faster query response times and improved overall throughput. Performance EvaluationFor this evaluation, we utilized three publicly available instance types on AWS:
By leveraging these diverse instance types, we aimed to evaluate the performance and efficiency of Milvus with CAGRA integration across different hardware configurations. The m6id.2xlarge instance served as a baseline for CPU-based performance, while the g4dn.2xlarge and g5.2xlarge instances allowed us to assess the benefits of GPU acceleration using the NVIDIA T4 and A10G GPUs, respectively. We used two publicly available vector datasets from VectorDBBench:
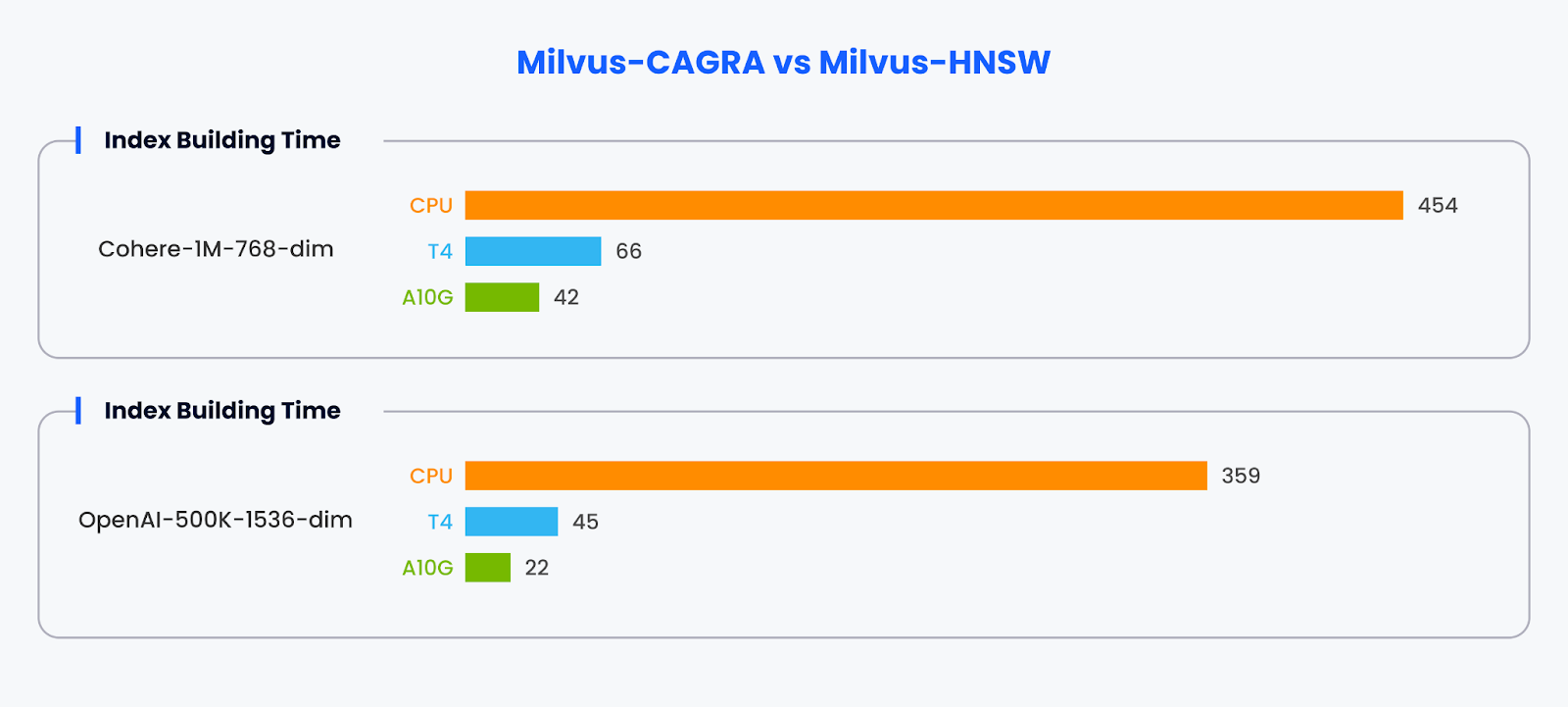
These datasets were specifically chosen to evaluate the performance and scalability of Milvus with CAGRA integration under different data volumes and vector dimensionalities. The OpenAI-500K-1536-dim dataset allows for assessing the system's performance with a moderately large dataset of extremely high-dimensional vectors. In contrast, the Cohere-1M-768-dim dataset tests the system's ability to handle larger volumes of moderately high-dimensional vectors. Index Building TimeWe compare the index-building time between Milvus with the CAGRA GPU acceleration framework and the standard Milvus implementation using the HNSW index on CPUs. For the Cohere-1M-768-dim dataset, the index building times are:
For the OpenAI-500K-1536-dim dataset, the index building times are:
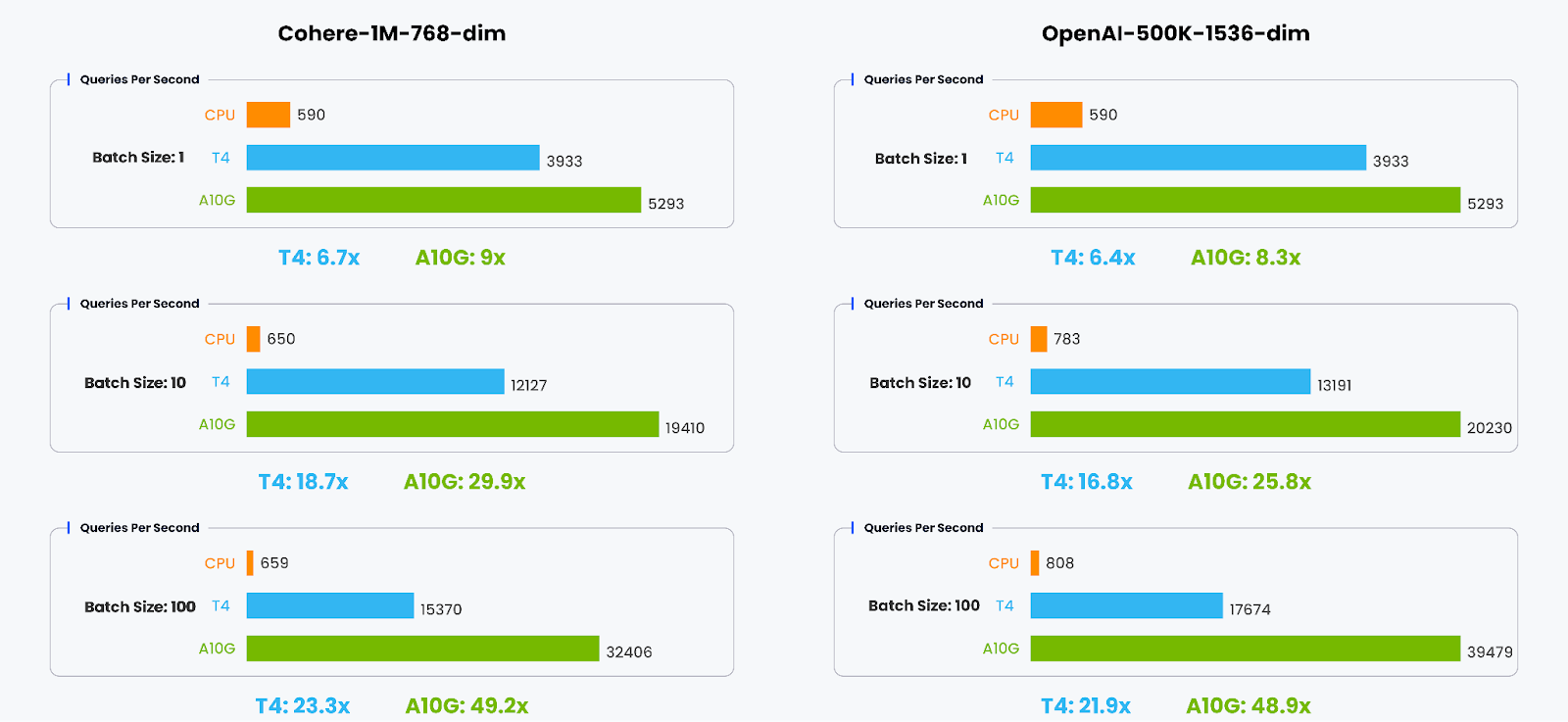
The results clearly show that CAGRA, the GPU-accelerated framework, significantly outperforms the CPU-based HNSW index building, with the A10G GPU being the fastest across both datasets. The GPU acceleration provided by CAGRA reduces the index building time by up to an order of magnitude compared to the CPU implementation, demonstrating the benefits of leveraging GPU parallelism for computationally intensive vector operations like index construction. ThroughputWe present a performance comparison between Milvus with the CAGRA GPU acceleration framework and the standard Milvus implementation using the HNSW index on CPUs. The metric being evaluated is Queries Per Second (QPS), which measures the throughput of query execution. We varied the batch size during the evaluation process, representing the number of queries processed concurrently, from 1 to 100. This comprehensive range of batch sizes allowed us to conduct a realistic and thorough evaluation, assessing the performance under different query workload scenarios. Looking at the charts, we can see that:
The results demonstrate the substantial performance gains achieved by leveraging GPU acceleration for vector database queries, particularly for larger batch sizes and higher-dimensional data. Milvus with CAGRA unlocks the parallel processing capabilities of GPUs, enabling significant throughput improvements and making it well-suited for demanding vector database workloads. Blazing New TrailsThe integration of NVIDIA's CAGRA GPU acceleration framework into Milvus 2.4 represents a groundbreaking achievement in vector databases. By harnessing GPUS’ massively parallel computing power, Milvus has unlocked unprecedented levels of performance for vector indexing and search operations, ushering in a new era of real-time, high-throughput vector data processing. The unveiling of Milvus 2.4, a collaboration between Zilliz and NVIDIA, exemplifies the power of open innovation and community-driven development by bringing GPU acceleration to vector databases. This milestone marks the beginning of a transformative era, where vector databases are poised to experience exponential performance leaps akin to NVIDIA's remarkable achievement of increasing GPU computing power by 1000x over the past eight years. In the coming decade, we will witness a similar surge in vector database performance, catalyzing a paradigm shift in how we process and harness the immense potential of unstructured data. *This post was written by Charles Xie, founder and CEO at Zilliz, specially for TheSequence. We thank Zilliz for their insights and ongoing support of TheSequence.You’re on the free list for TheSequence Scope and TheSequence Chat. For the full experience, become a paying subscriber to TheSequence Edge. Trusted by thousands of subscribers from the leading AI labs and universities. |
Older messages
NVIDIA’s GTC in Four Headlines
Sunday, March 24, 2024
Impressive AI hardware innovations and interesting software moves. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
📌 Exciting lineup for apply() 2024 is now live
Friday, March 22, 2024
Exciting news! The agenda for apply() 2024, Tecton's premier virtual conference dedicated to mastering AI and ML at production scale, is now live! Join us on Wednesday, April 3, for a day packed
Edge 380: Inside SELF-Discover: Google DeepMind's LLM Reasoning Method for Solving Complex Tasks
Thursday, March 21, 2024
The techniques addresses some of the limitation of prompting methods such as chain-of-thought. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
Edge 379: A Summary Of Our Series About LLM Reasoning
Tuesday, March 19, 2024
In 13 issues, this series covered the fundamental concepts, research and tech around reasoning in LLMs. ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
Explore the Global Generative AI Landscape 2024 by AIport
Monday, March 18, 2024
Our friends from AIport – an online community of AI writers and practitioners – have just released Volume I of the Global Generative AI Landscape 2024. This landscape provides a comprehensive analysis
You Might Also Like
Import AI 399: 1,000 samples to make a reasoning model; DeepSeek proliferation; Apple's self-driving car simulator
Friday, February 14, 2025
What came before the golem? ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
Defining Your Paranoia Level: Navigating Change Without the Overkill
Friday, February 14, 2025
We've all been there: trying to learn something new, only to find our old habits holding us back. We discussed today how our gut feelings about solving problems can sometimes be our own worst enemy
5 ways AI can help with taxes 🪄
Friday, February 14, 2025
Remotely control an iPhone; 💸 50+ early Presidents' Day deals -- ZDNET ZDNET Tech Today - US February 10, 2025 5 ways AI can help you with your taxes (and what not to use it for) 5 ways AI can help
Recurring Automations + Secret Updates
Friday, February 14, 2025
Smarter automations, better templates, and hidden updates to explore 👀 ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏ ͏
The First Provable AI-Proof Game: Introducing Butterfly Wings 4
Friday, February 14, 2025
Top Tech Content sent at Noon! Boost Your Article on HackerNoon for $159.99! Read this email in your browser How are you, @newsletterest1? undefined The Market Today #01 Instagram (Meta) 714.52 -0.32%
GCP Newsletter #437
Friday, February 14, 2025
Welcome to issue #437 February 10th, 2025 News BigQuery Cloud Marketplace Official Blog Partners BigQuery datasets now available on Google Cloud Marketplace - Google Cloud Marketplace now offers
Charted | The 1%'s Share of U.S. Wealth Over Time (1989-2024) 💰
Friday, February 14, 2025
Discover how the share of US wealth held by the top 1% has evolved from 1989 to 2024 in this infographic. View Online | Subscribe | Download Our App Download our app to see thousands of new charts from
The Great Social Media Diaspora & Tapestry is here
Friday, February 14, 2025
Apple introduces new app called 'Apple Invites', The Iconfactory launches Tapestry, beyond the traditional portfolio, and more in this week's issue of Creativerly. Creativerly The Great
Daily Coding Problem: Problem #1689 [Medium]
Friday, February 14, 2025
Daily Coding Problem Good morning! Here's your coding interview problem for today. This problem was asked by Google. Given a linked list, sort it in O(n log n) time and constant space. For example,
📧 Stop Conflating CQRS and MediatR
Friday, February 14, 2025
Stop Conflating CQRS and MediatR Read on: my website / Read time: 4 minutes The .NET Weekly is brought to you by: Step right up to the Generative AI Use Cases Repository! See how MongoDB powers your